- Product
- A product is any good or service that satisfies the needs or wants of consumers
- Either tangible (physical products) or intangible (services)
- Must have value added (either functional value or emotional value)
- Functional – Useful
- Emotional – Appeals to emotion (instills pride, happiness, etc.)
- A product is any good or service that satisfies the needs or wants of consumers
- Types of products
- Consumer products – products sold directly to consumers
- Fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG)
- Sells by large quantitiesSoap, shampoo, pencils, etc.Usually cheap
- Seasonal products
- Fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG)
- Consumer products – products sold directly to consumers
- Products with limited shelf-life
- Can be sold at a higher price compared to FMCG since they are a premium
- Long lasting and relatively expensive products
- Since they are long lasting, not as many are sold, so they are more expensive
- Most expensiveUnique products
- Low Involvement Product (LIP)
- Opposite of HIP
- Consumer will take a while to decide when purchasing
- Producer Products
- Goods purchased by businesses for production process (raw materials & inputs)
- Product life cycle
- Pertains to the different stages of a product’s lifespan
- Measured in terms of sales level and growth phases over a period of time.Used to identify necessary changes in marketing strategies
- Each stage will usually need a different marketing mix
- Research and development
- Design, development and testing
- Measured in terms of sales level and growth phases over a period of time.Used to identify necessary changes in marketing strategies
- Requires a large investment in resources and time
- Creation of prototype with feedback from target market
- Alpha and Beta releases for testing
- Product will be priced HIGH to cover
- Costs of heavy marketing
- Creation of prototype with feedback from target market
- Cost of research and development
- Rapid volume increase due to better awareness and expansion of distribution channelsStarts to be profitable due to economies of scale in production and marketingCompetition begins becoming attracted to the market
- Sales may begin to peak/stabilize (no significant changes)Achieve highest market share, while competition continues to pour into the market
- Companies will employ price reductions, product differentiation and extension strategies very aggressively to protect their market share
- Sales and profits decline due to shifts in demand, new technology, or new models
- Price levels fall (to get rid of inventory) prior to withdrawal
- Phasing out the product
- Price levels fall (to get rid of inventory) prior to withdrawal
- Price reduction
- Redesigns (e.g. special features, limited edition, etc.)Repacking (e.g. new colors, materials)New markets/market developmentPromotions (advertising and special tie-ups)
- Aside from demographic/psychographics, speed of adoption is also affected by
- Relative advantage
- Compatibility
- Testability
- Observable feature
- Convenience
- Product life cycle and the marketing mix
- Launch
- Price: may be high or low compared to competitorsPromotion: high levels of informative advertising to make the consumers aware of the product’s arrival on the marketPlace: restricted outlets – possibly high-class outlets if a skimming strategy is adopted
- Launch
- Product: basic model
- Price: if successful, an initial penetration pricing strategy could now lead to rising pricesPromotion: consumers need to be convinced to make repeat purchases- brand identification will help to establish consumer loyaltyPlace: growing numbers of outlets in areas indicated by strength of consumer demand
- Product: planning of product improvements and developments to maintain consumer appeal
- Price: competitors likely to be entering market – there will be a need to keep prices at competitive levelsPromotion: brand Imaging continues growing – need to stress the positive differences with competitor’s products
- Place: highest geographical range of outlets as possible – developing new types of outlets where possible
- Product: new models, colors, accessories, etc. as part of extension strategy
- Decline
- Price: lower prices to sell off stock-or if the product has a small ‘cult’ following, prices could even risePromotion: advertising likely to be very limited – may just be used to inform of lower price
- Place: eliminate unprofitable outlets for the product
- Product: prepare to replace with other products – slowly withdraw
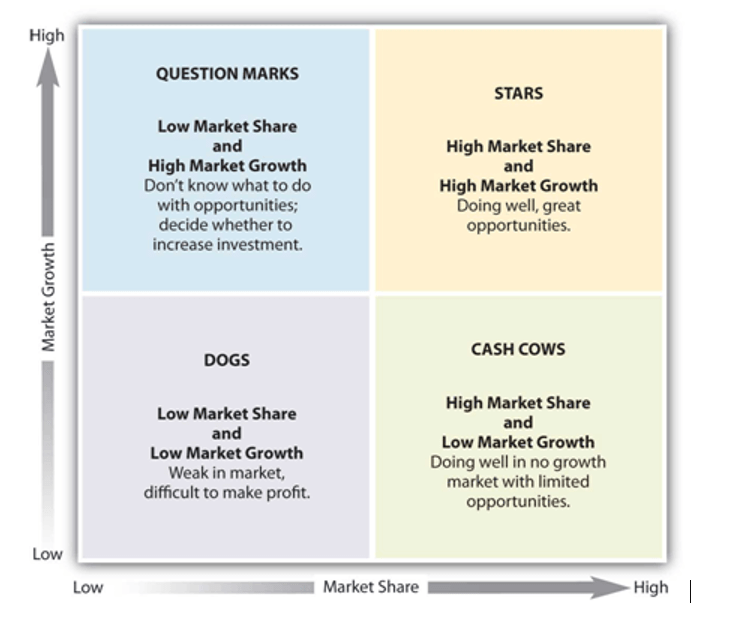
- Boston Consulting Group (BCG) matrix
- Planning tool used to classify a portfolio of products based on market share and market growth
- Problem child/question mark
- High growth market but low market share
- Problem child/question mark
- More resources must be used (cash absorbing) to gain higher market share
- Alternative is to divest and use resources to help other products
- To do nothing will make this a dog
- It can become a star or dog
- High growth market with high market share
- Generate a lot of cash and profit but require marketing support
- If position is maintained, it may turn into a cash cow
- If not, may become problem child
- Low growth market but high market share
- Products that command a high share of the market despite maturity
- Well-establishedGenerate good cash flow and strong profitsNo further investments required although extension strategies may be used to delay decline
- May be used to pay dividends, debts, support problem child products, stars or new product development
- Low growth market with a low market share
- Product in a mature market
- Does not generate much revenue
- Ties up cash (capital), may be withdrawn or repositioned to niche market where more premium price can be demanded
- Strategic analysis
- Used to support your products
- Building – support problem childs
- Holding – try to maintain the position
- Milking – using cash cows
- Divesting – getting rid of dogs
- Can only be undertaken if business has a balanced portfolio of products.
- All 4 quadrants must be filled
- Dogs or problem children outnumbering stars and cash cows may lead to a cash shortage preventing the firm to take appropriate action
- Used to support your products
- Branding
- Name identifiable to a product or a mixture of tangible and intangible attributes symbolized in a trademark in order to differentiate the product from competitors
- Role and benefits
- Legal instrumentDifferentiationRisk reducerImage enhancerSales generatorGrowth platformTimeless
- An effective brand name can be a stimulus for positive association with the product; should be memorable, recognizable, and portray the desired image
- Role and benefits
- Aspects of branding
- Brand awareness
- An important aspect in being able to successfully promote a product
- Brand awareness
- Essential in markets with products that have very few tangible factors that differentiate products from one another
- Long term marketing strategy meant to build and strengthen the image
- A strong brand can extend maturity or cash cow position of a product (sustain and increase sales)
- Customers favoring a brand over rivalsQuantifies effect of marketing activities
- When customers buy products of the same brand repeatedlyBenefits:
- Higher market share
- Premium pricing by keeping loyal customers
- Demand is more price inelastic
- Customers are not sensitive to price changes
- Demand is more price inelastic
- Raises barriers to entry
- New players find it hard to gain a market
- Raises barriers to entry
- Brand value
- The value added premium that customers are willing to pay for a product of a well known brand as opposed to a generic equivalent
- Mass promotion campaigns are essential to help create brand value
- Is important if a business would like to expand its product line
- Can help assure sales if current products within the brand have experienced relatively good success/popularity with customers
- Packaging
- Serves as protection for the product before reaching the end consumer
- Makes it easier, more efficient, and safer to transport
- Attraction, promotion, and differentiation
- Makes it eye-catching, amongst dozens of other similar products on a shelf
- Design theme, color scheme,
- How to use the product
- Makes it eye-catching, amongst dozens of other similar products on a shelf
- Materials/ingredients usedHighlights important features
- Helps to promote the brand and its image